Introducing Profunda Health
In Latin and in several Romance languages, profunda means "deep" or "coming from the depths." This term originates from Latin, where "profunda" is the feminine form of "profundus," and it has been preserved with similar meanings across the Romance language family including Spanish, Portuguese and Italian. In all these languages, the word consistently conveys a sense of depth, whether referring to physical depth or metaphorical profoundnes.
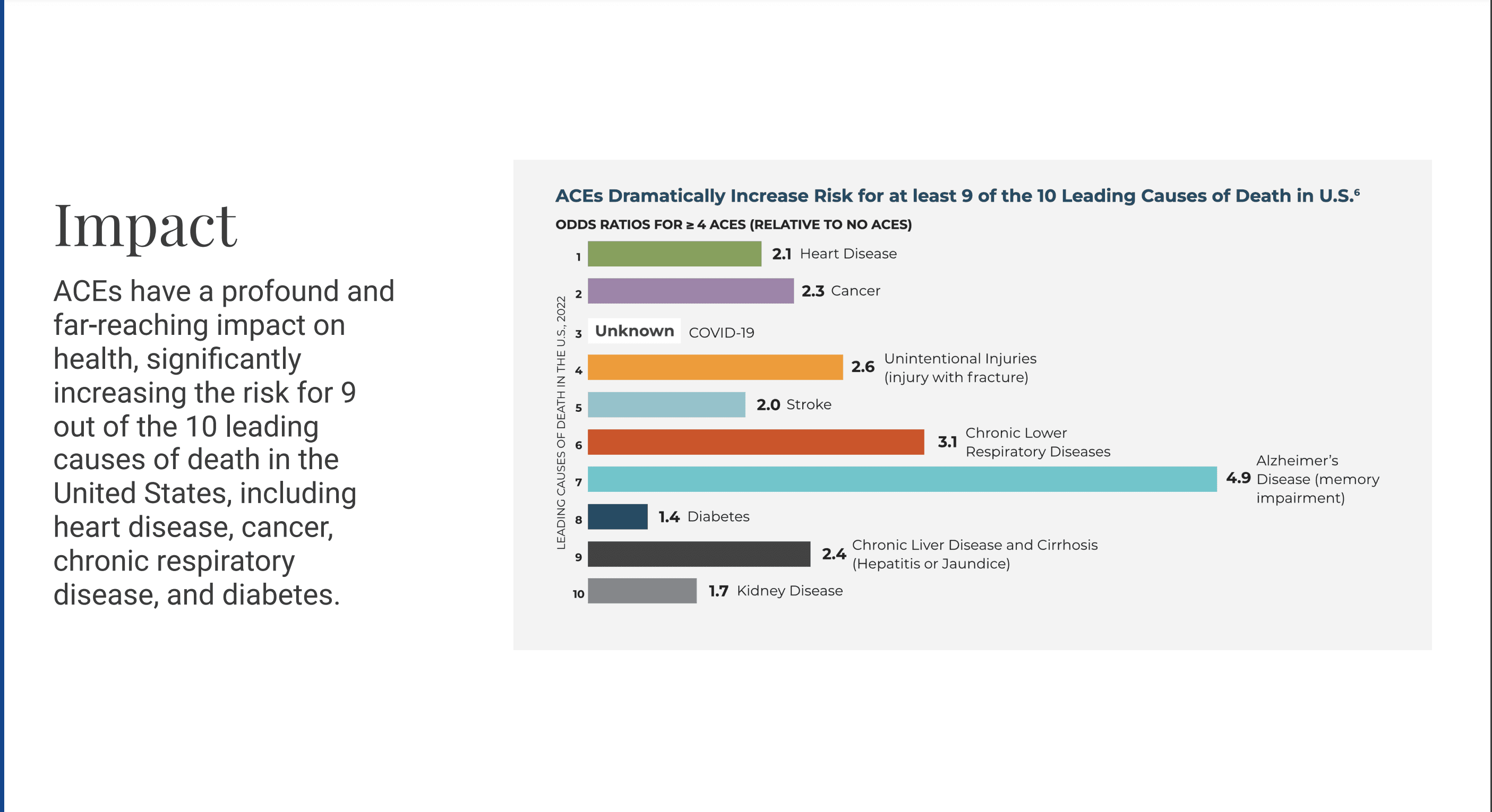
That is why today, we're proud to introduce Profunda Health – our first market-ready solution addressing the $14 trillion economic burden of Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) in the United States.
We remain Cepanoa Health – a name that means "to come together" in Nahuatl – honoring our core mission of building community around healing. Profunda represents our new product line that embodies this collective approach while diving deeper into personalized care.
At the core of our approach is a nuanced understanding of childhood adversity and its impacts. Our comprehensive ACEs assessment provides insight into how early experiences affect your current well-being by evaluating different types of adversity before age 18:
0: No identified childhood adversity from measured categories
1-3: Some exposure to childhood adversity
4+: Significant exposure, indicating increased risk for health and social challenges
Unlike platforms that simply calculate an ACEs score and leave you wondering "what now?", Profunda creates accessible healing pathways for everyone. Whether you're just beginning to explore your childhood experiences or seeking intensive support for complex trauma, our tiered approach ensures you receive the right resources at the right time. We've designed Profunda to break down barriers to trauma-informed care – making healing accessible regardless of geography, prior knowledge, or healthcare access.
To further support users, we have included a comprehensive list of resources related to each ACEs question, along with scientific research and articles from medical professionals, health experts, and doctors. These resources offer deeper insights into the effects of childhood adversity and evidence-based strategies for resilience and recovery.
Remember: Your ACE score isn't destiny. Many people with high scores lead fulfilling lives, especially with appropriate support and healing resources. People can still have a lasting impact on
Beyond Surface-Level Wellness
Unlike conventional approaches, Profunda Health targets how childhood trauma embeds itself in our bodies, minds, and relationships. Our comprehensive platform delivers:
Integrated Care Pathways: Seamlessly connecting social support, education, and clinical care
Tiered Support: Meeting members at their current stage with appropriate resources
Precision Health Technology: Creating personalized healing journeys through advanced assessments, including biomarker insights.
The Lasting Impact of Childhood Trauma
The groundbreaking ACEs study by Kaiser Permanente and the CDC revealed how early traumatic experiences correlate with lifelong health and social challenges:
Chronic health conditions (heart disease, diabetes, autoimmune disorders)
Mental health challenges (depression, anxiety, PTSD)
Relationship difficulties and attachment issues
Emotional regulation problems
Addictive behaviors
Understanding these connections isn't about blame—it's the first step toward healing.
Your Healing Journey
Healing from childhood trauma requires both courage and support. Our process guides you through:
Acknowledging your experiences
Understanding connections between past trauma and present challenges
Processing difficult emotions in a supportive environment
Integrating experiences into your life story with new meaning
Growing into new patterns and possibilities
Take the First Step
We invite you to join us on this journey of healing and transformation. Your path to wellness begins here.
Disclaimer: This post is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. The ACEs assessment is not a diagnostic tool; while high ACE scores are linked to increased health risks, they do not determine individual outcomes. Profunda Health complements, not replaces, professional healthcare services. If you are in distress or experiencing thoughts of self-harm or harm to others, please seek immediate help—contact your healthcare provider, call 988 (Suicide & Crisis Lifeline), or visit the nearest emergency room
Today, we want to shed light on a critical and often overlooked connection: the relationship between Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) and kidney disease. ACEs are traumatic events that occur before the age of 18, such as:
physical, sexual, or emotional abuse, neglect and/or household dysfunction (divorce, substance abuse, mental illness, incarceration) and community violence.
Many people don't realize that these experiences are not just emotional scars – they have profound physiological consequences that can manifest decades later.
Research has uncovered a startling link between high ACE scores and increased risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Here's what we're learning:
Chronic Stress and Physiological Changes: Repeated childhood trauma triggers prolonged stress responses, leading to:
- Elevated cortisol levels
- Chronic inflammation
- Dysregulated immune system
- Altered stress response pathways
- Epigenetic changes affecting kidney cell function
- Increased risk of hypertension and diabetes
We cannot change the past, but we can reshape the future. Recognizing the long shadow of ACEs on kidney health is a critical step toward prevention, early intervention, and more compassionate care. As advocates, healthcare providers, and community members, we have the power to tell our doctors about our ACEs.
Join Cepanoa Health to learn more.
The Intersecting Landscape of Trauma and Immune Health
Women face a unique and complex health challenge at the intersection of psychological trauma and immune system dysfunction. Emerging research reveals a profound connection between Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) and the increased risk of autoimmune diseases, highlighting the critical need for a holistic understanding of women's health.
The Disproportionate Impact
Gender Disparities in Autoimmune Conditions
Women represent approximately 80% of all autoimmune disease patients
Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Hashimoto's thyroiditis predominantly affect women.
The female-to-male ratio in autoimmune diseases ranges from 3:1 to as high as 9:1 for some conditions
Biological Mechanisms: Stress, Trauma, and Immune Dysregulation
The Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) Axis and Immune Response
Chronic stress from childhood trauma fundamentally alters the body's stress response system:
Prolonged activation of the HPA axis leads to persistent inflammatory responses
Cortisol dysregulation can cause immune system hypersensitivity
Epigenetic changes may reprogram immune cell functioning
Neuroinflammatory Pathways
Childhood trauma triggers persistent neuroinflammatory processes
Increases pro-inflammatory cytokine production
Disrupts neural communication pathways that regulate immune responses
Epidemiological Evidence
A landmark study published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine demonstrated that:
Individuals with four or more ACEs have a 70% higher likelihood of developing autoimmune diseases
Childhood psychological trauma correlates with a 2-3 times increased risk of autoimmune conditions
Cumulative ACEs show a dose-response relationship with immune system dysfunction
Psychological and Physiological Interconnections
Stress-Induced Immune Modulation
Chronic psychological stress suppresses natural killer cell activity
Reduces lymphocyte proliferation
Increases systemic inflammation markers
Neuroendocrine Disruption
Traumatic experiences alter hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis functioning
Impacts cortisol production and inflammatory response regulation
Creates a persistent state of immune system hypervigilance
Clinical Implications and Whole-Woman Interventions
Recommended Comprehensive Approaches
Trauma-Informed Medical Care
Screening for ACEs in comprehensive health assessments
Integrating mental health support with medical treatment
Developing personalized intervention strategies
Interdisciplinary Treatment Models
Combining psychological therapies with immunomodulatory treatments
Stress reduction techniques like mindfulness and cognitive-behavioral therapy
Nutritional psychiatry focuses on the relationship between diet and mental health, exploring how nutrients impact brain function, mood, and mental disorders. It emphasizes using food and supplements as part of treatment for conditions like depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline.
Future Research Directions
Investigating precise molecular mechanisms linking childhood trauma to autoimmune diseases
Developing targeted interventions for early prevention
Exploring personalized medicine approaches based on individual trauma histories
Conclusion
Understanding the intricate relationship between Adverse Childhood Experiences and autoimmune diseases represents a critical frontier in women's health research. By recognizing the profound mind-body connection, healthcare professionals can develop more nuanced, compassionate, and effective treatment strategies.
Key Takeaway: Childhood trauma is not just a psychological event but a potential biological catalyst with long-lasting immunological consequences.
We’re beyond excited to announce that Cepanoa Health has officially emerged from stealth mode! After months of behind-the-scenes innovation, we’re now ready to take the next bold step: recruiting participants for our exclusive beta program. This marks a major milestone in our mission to transform how we address the lasting effects of Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) by focusing on early intervention and whole-family care.
For too long, ACEs have quietly but profoundly impacted millions of lives. ACEs refer to traumatic events such as abuse, neglect, or household dysfunction during childhood, and their consequences can extend well into adulthood. The effects of ACEs are far-reaching, contributing to serious health issues like heart disease, depression, anxiety, and PTSD. Research shows that over 63% of adults have experienced at least one ACE, and individuals with multiple ACEs are at a significantly higher risk for chronic conditions, mental health disorders, and even reduced life expectancy.
ACEs cause toxic or chronic stress. Allostatic load is the cumulative wear and tear on the body’s systems due to chronic stress. When a person is exposed to prolonged stress, their body constantly adapts to cope with it, but over time, this constant adaptation can lead to physiological dysregulation. This includes hormonal imbalances, immune function, and other bodily systems, which can contribute to various health issues.
Instead of focusing on high-risk behaviors, it’s more insightful to examine how prolonged toxic stress—triggered by external or internal factors—affects the body on a deeper, biological level. This kind of stress can disrupt homeostasis, leading to allostatic load, which manifests in physical, emotional, and cognitive dysregulation. It’s less about individual choices or behaviors and more about how chronic exposure to stress impairs bodily systems like cardiovascular, metabolic, and immune functions. Left unaddressed, these early adversities not only burden the individual but also create massive healthcare and economic costs, amounting to an estimated $14.1 trillion annually in the U.S. alone .
At Cepanoa Health, we are addressing these challenges by focusing on prevention, early intervention, and evidence-based care. Our mission is to reduce the lifelong health risks associated with ACEs by providing personalized, trauma-informed healthcare solutions
At Cepanoa, we’re building the first comprehensive platform dedicated to addressing these challenges. Using AI-powered tools, we aim to help families and healthcare providers prevent and manage the impacts of ACEs through trauma-informed care.
Our platform offers a unique approach to early intervention by integrating family health assessments, evidence-based therapies, and personalized support. This proactive model helps prevent ACE-related conditions from becoming long-term burdens, empowering families and providers with the tools needed to thrive.
Join our Beta Program
As we open up our platform to a select group of early adopters, we invite you to join our Beta program and be part of this revolutionary solution. By participating, you’ll not only gain early access but also play a key role in shaping the future of ACEs healthcare.
Sign up for our Beta program waitlist here and help us bring high-quality, scalable care to those who need it most.
Together, we can tackle ACEs and transform healthcare for future generations.




